DocSignTool is a secure, privacy-oriented multi-platform Java command line utility for remotely signing PDF files using eSigner document signing certificates. Hashes of the documents are sent to SSL.com for signing so that the document itself is not sent. This is ideal where sensitive documents need to be signed, but should not be sent over the wire for signing. DocSignTool is also ideal for automated batch processes for high volume signings or integration into existing document workflows.
If you are looking to use esigner to sign code and excutables instead, please refer to this CodeSignTool guide.
DocSignTool Installation
To install the current version of DocSignTool, simply download and unzip the correct file for your OS:
Note that the Windows download includes Java runtime, but the Linux/macOS version requires Java runtime to be installed on your computer. The Windows version of the command is a batch file (DocSignTool.bat) and the Linux/macOS version is a shell script (DocSignTool.sh).
DocSignTool Usage Overview
Usage: DocSignTool [-hV] [COMMAND] [PARAMETERS]
Options:
-h,--help: Display help message and exit.-V,--version: Display version information and exit.
Commands:
get_credential_ids: Output the list of eSigner credential IDs associated with a particular user.credential_info: Output key and certificate information related to a credential ID.sign: Sign and timestamp PDF filr.batch_sign: Sign and timestamp multiple PDF files with one OTP.hash: Pre-compute hash(es) for later use withbatch_hash_signcommand.batch_sign_hash: Sign hash(es) pre-computed withhashcommand.
Parameters:
-access_token=<TOKEN>: OAuth access token.-contact_info=<CONTACT_INFO>: Contact information.-credential_id=<CREDENTIAL_ID>: Credential ID for signing certificate.-input_dir_path=<PATH>: Input directory for PDF files to be signed, have hashes computed, or pick unsigned files and corresponding hashes for signing.-input_file_path=<PATH>: Path of PDF file to be signed.-otp=<OTP>: OAuth OTP value from authentication app.-output_dir_path=<PATH>: Directory where signed PDF file(s) will be written.-page_no=<PAGE_NUMBER>: Page of PDF document where visible signature will appear.-password=<PASSWORD>: SSL.com account password.-sig_field_position=<X, Y, WIDTH, HEIGHT>: Position of visible signature on PDF.-signing_location=<SIGNING_LOCATION>: Location where document is signed.signing_reason=<SIGNING_REASON>: Reason for signing.-totp_secret=<TOTP_SECRET>: OAuth TOTP secret-username=<USERNAME>: SSL.com account username
-password="P!@^^ssword12").DocSignTool Commands
get_credential_ids
Output the list of eSigner credential IDs associated with a particular user. Parameters -username and -password are required.
Usage: DocSignTool [-hV] get_credential_ids -username=<USERNAME> -password=<PASSWORD>
Example:
Entering DocSignTool get_credential_ids without the required parameters will display usage information for the command.
credential_info
Output key and certificate information related to a credential ID. Parameters -credential_id, -username, and -password are required.
Usage: DocSignTool [-hV] credential_info -credential_id=<CREDENTIAL_ID> -username=<USERNAME> -password=<PASSWORD>
Example:
Entering DocSignTool credential_info without the required parameters will display usage information for the command.
sign
Sign and timestamp PDF file. Parameters -username, -password, and -input_file_path are required. -credential_id is required only for users with more than one eSigner document signing certificate. -output_dir_path, -signing_location, -signing-reason, -contact_info, -sig_field_position, -page_no, and -totp_secret are optional.
Usage: DocSignTool sign [-hV] [-credential_id=<CREDENTIAL_ID>] -username=<USERNAME> -password=<PASSWORD> -input_file_path=<PATH> [-output_dir_path=<PATH>] [-signing_location=<SIGNING_LOCATION>] [-signing_reason=<SIGNING_REASON>] [-contact_info=<CONTACT_INFO>] [-sig_field_position=<X, Y, WIDTH, HEIGHT>][-page_no=<PAGE_NUMBER>] [-totp_secret=<TOTP_SECRET>]
Optional parameters:
- If
-credential_idis omitted and the user has only one eSigner document signing certificate, DocSignTool will default to that. If the user has more than one document signing certificate, this parameter is mandatory. - If
-output_dir_pathis omitted, the file specified in-input_file_pathwill be overwritten with the signed file. DocSignTool will prompt the user before overwriting the file. - If
-signing_locationis present, the location specified will be added to the digital signature. - If
-signing_reasonis present, the reason for signing specified will be added to the digital signature. - If
-contact_infois present, the specified text will be added to the digital sigature. Although included with the signature, this information will not be included in the visible signature annotation (if present). - If
-sig_field_positionis present, a visible signature annotation will be added to the document on the page specified by-page_no. The position and signature should be supplied in the format"x, y, width, height". -page_nois only required when creating a visible signature with-sig_field_positionand specifies the page of the document that the visible signature annotation will appear on.- If
-totp_secretis present, DocSignTool will calculate a time-based OTP for signing, allowing automated use of the tool. If this parameter is not present, the user will be prompted for manual OTP entry.
Examples:
Manual OTP Entry with Visible Signature:
Automated OTP Generation, No Visible Signature:
Entering DocSignTool sign without the required parameters will display usage information for the command.
- The QR code you scanned into your authentication app doesn’t match the username, password, and/or credential ID from your command. This could happen if:
- You have multiple accounts configured for 2FA on your device and chose the wrong one.
- You are attempting to use your login credentials for a shared certificate, but scanned a QR code shared by a teammate from their account.
- The OTP you entered has already expired.
- Your command includes an invalid TOTP secret.
batch_sign
Sign and timestamp up to 100 PDF files with one OTP. Parameters -username, -password, and -input_dir_path are required. -credential_id is required only for users with more than one eSigner document signing certificate. -output_dir_path, -signing_location, -signing-reason, -contact_info, -sig_field_position, -page_no, and -totp_secret are optional.
Usage: DocSignTool [-hV] batch_sign [-hV] [-credential_id=<CREDENTIAL_ID>] -username=<USERNAME> -password=<PASSWORD> -input_dir_path=<PATH> [-output_dir_path=<PATH>] [-signing_location=<SIGNING_LOCATION>] [-signing_reason=<SIGNING_REASON>] [-contact_info=<CONTACT_INFO>] [-sig_field_position=<X, Y, WIDTH, HEIGHT>][-page_no=<PAGE_NUMBER>] [-totp_secret=<TOTP_SECRET>]
Optional parameters:
- If
-credential_idis omitted and the user has only one eSigner document signing certificate, DocSignTool will default to that. If the user has more than one document signing certificate, this parameter is mandatory. - If
-output_dir_pathis omitted, the files specified in-input_dir_pathwill be overwritten with the signed files. DocSignTool will prompt the user before overwriting the files. - If
-signing_locationis present, the location specified will be added to the digital signatures. - If
-signing_reasonis present, the reason for signing specified will be added to the digital signatures. - If
-contact_infois present, the specified text will be added to the digital sigatures. Although included with the signature, this information will not be included in the visible signature annotations (if present). - If
-sig_field_positionis present, a visible signature annotation will be added to the documents on the page specified by-page_no. The position and signature should be supplied in the format"x, y, width, height". -page_nois only required when creating a visible signature with-sig_field_positionand specifies the page of the documents that the visible signature annotations will appear on.- If
-totp_secretis present, DocSignTool will calculate a time-based OTP for signing, allowing automated use of the tool. If this parameter is not present, the user will be prompted for manual OTP entry.
Example:
Entering DocSignTool batch_sign without the required parameters will display usage information for the command.
hash
- A PDF library is needed to manipulate the PDF for hash input and later embed the PKCS#7 in the PDF document. (ex. ApachePDFBox in Java).
- A Crypto library for creating PKCS#7 out of raw signatures received from eSigner API (ex. BouncyCastle in Java).
Pre-compute hash(es) for later use with batch_hash_sign command. Parameters -access_token and -input_dir_path are required. -credential_id is required only for users with more than one eSigner document signing certificate. -signing_location, -signing-reason, -contact_info, -sig_field_position, and -page_no, are optional.
Usage: DocSignTool [-hV] hash -access_token=<ACCESS_TOKEN> -input_dir_path=<PATH> [-signing_location=<SIGNING_LOCATION>] [-signing_reason=<SIGNING_REASON>] [-contact_info=<CONTACT_INFO>] [-sig_field_position=<X, Y, WIDTH, HEIGHT>][-page_no=<PAGE_NUMBER>]
Optional parameters:
- If
-program_nameis present when signing an MSI installer, the value will be displayed in the confirmation dialog as the program name. - If
-signing_locationis present, the location specified will be added to the digital signatures when they are generated. - If
-signing_reasonis present, the reason for signing specified will be added to the digital signatures when they are generated. - If
-contact_infois present, the specified text will be added to the digital sigatures when they are generated. Although included with the signature, this information will not be included in the visible signature annotations (if present). - If
-sig_field_positionis present, a visible signature annotation will be added to the documents on the page specified by-page_nowhen the signatures are generated. The position and signature should be supplied in the format"x, y, width, height". -page_nois only required when creating a visible signature with-sig_field_positionand specifies the page of the documents that the visible signature annotations will appear on when they are generated.
Example:
Entering DocSignTool hash without the required parameters will display usage information for the command.
batch_sign_hash
Sign hash(es) pre-computed with hash command. Parameters -access_token, input_dir_path, -otp, and output_dir_path are required. -credential_id is required only for users with more than one eSigner document signing certificate.
Usage: DocSignTool [-hV] batch_sign_hash -access_token=<ACCESS_TOKEN> [-credential_id=<CREDENTIAL_ID>] -input_dir_path=<PATH> -output_dir_path=<PATH> -otp=<OTP>
Optional parameters:
- If
-credential_idis omitted and the user has only one eSigner document signing certificate, DocSignTool will default to that. If the user has more than one document signing certificate, this parameter is mandatory.
Example:
Entering DocSignTool batch_sign_hash without the required parameters will display usage information for the command.
How to test DocSignTool in sandbox mode
- In the DocSignTool release, go to
conffolder and opendoc_sign_tool.propertiesfile - Comment out the existing properties by adding
#symbol before every property - Add the following properties in the file:
CLIENT_ID=qOUeZCCzSqgA93acB3LYq6lBNjgZdiOxQc-KayC3UMwOAUTH2_ENDPOINT=https://oauth-sandbox.ssl.com/oauth2/tokenCSC_API_ENDPOINT=https://cs-try.ssl.comTSA_URL=http://ts.ssl.com
- Save the file. After saving, DocSignTool can now be used in sandbox mode.
- To switch back to production mode, uncomment the existing properties and delete the sandbox properties.
Optional: Convert your OV document signing certificate to an esealing certificate
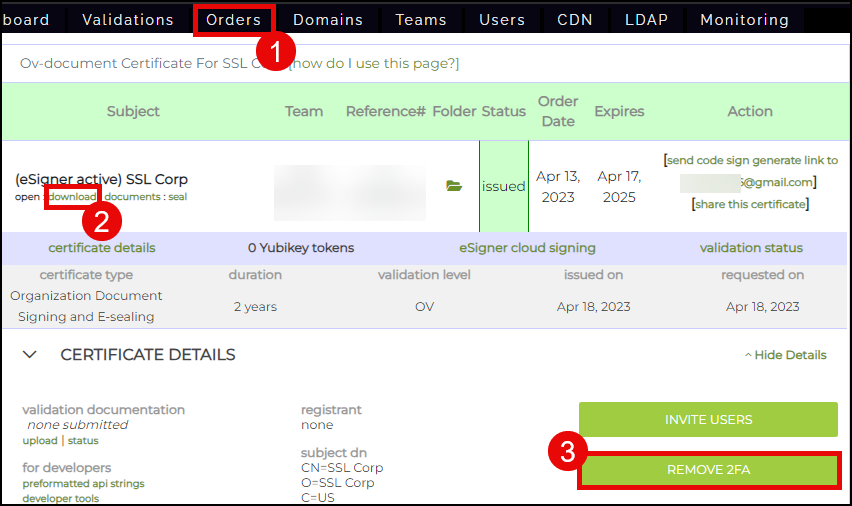
Note: This section is only for users who want to do esealing. To automate document signing and not be prompted by One Time Passwords (OTP), users self-convert their Organization Validation (OV) document signing certificate to an esealing certificate on their SSL.com accounts. Instructions are below:
- Click Orders on the top menu of your SSL.com account.
- Locate your certificate and click the download/details link.
- Click the REMOVE 2FA button.